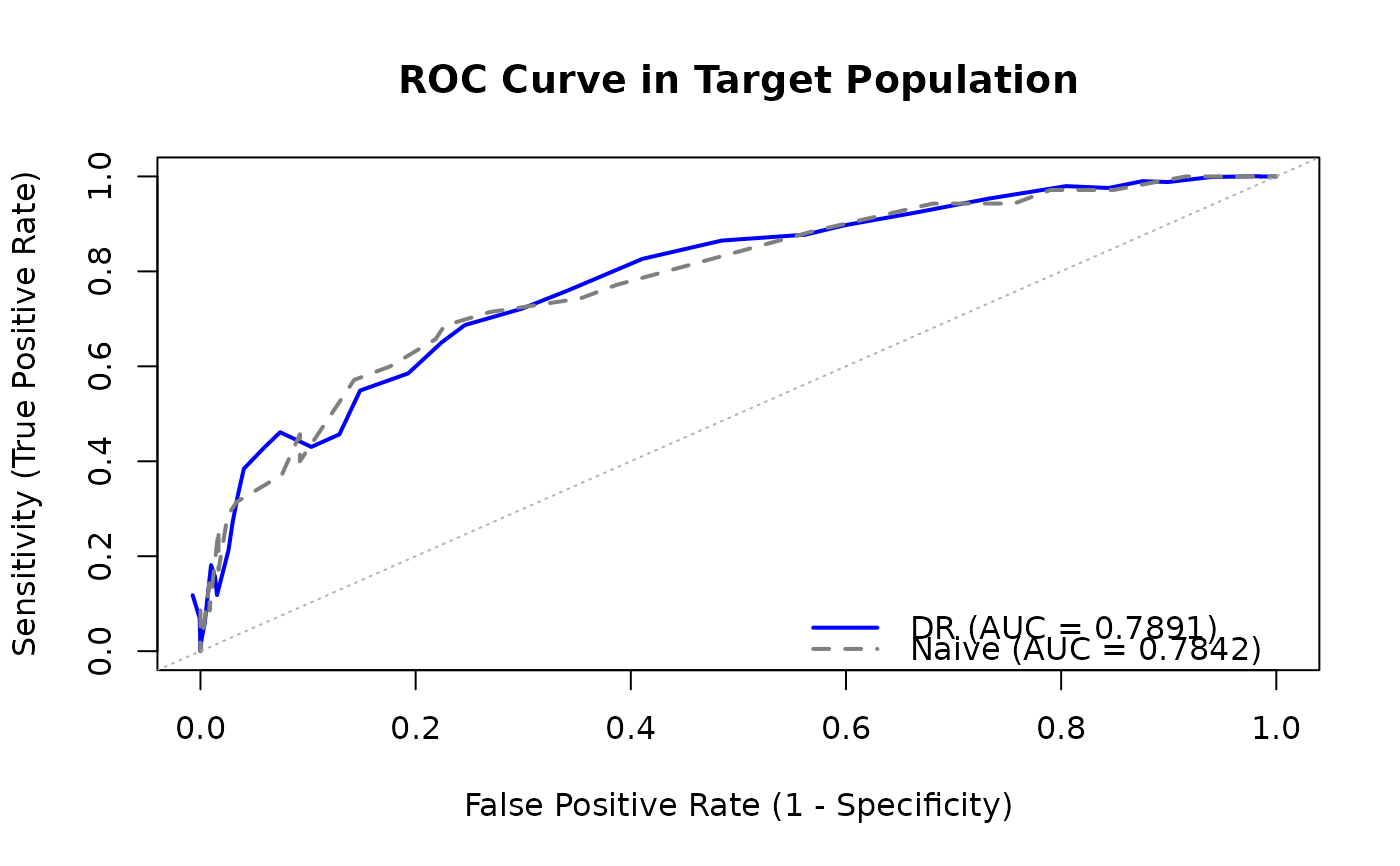
Computes a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in a target population using data transported from a source population. Returns sensitivity (TPR) and false positive rate (FPR) at multiple thresholds. Supports both counterfactual and factual prediction model transportability.
Usage
tr_roc(
predictions,
outcomes,
treatment = NULL,
source,
covariates,
treatment_level = NULL,
analysis = c("transport", "joint"),
estimator = c("dr", "om", "ipw", "naive"),
selection_model = NULL,
propensity_model = NULL,
outcome_model = NULL,
n_thresholds = 201,
thresholds = NULL,
include_naive = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- predictions
Numeric vector of model predictions.
- outcomes
Numeric vector of observed outcomes.
- treatment
Numeric vector of treatment indicators (0/1), or
NULLfor factual prediction model transportability (no treatment/intervention). WhenNULL, only the selection model is used for weighting.- source
Numeric vector of population indicators (1=source/RCT, 0=target).
- covariates
A matrix or data frame of baseline covariates.
- treatment_level
The treatment level of interest (default:
NULL). Required whentreatmentis provided; should beNULLwhentreatmentisNULL(factual mode).- analysis
Character string specifying the type of analysis:
"transport": Use source outcomes for target estimation (default)"joint": Pool source and target data
- estimator
Character string specifying the estimator:
"naive": Naive estimator (biased)"om": Outcome model estimator"ipw": Inverse probability weighting estimator"dr": Doubly robust estimator (default)
- selection_model
Optional fitted selection model for P(S=0|X). If NULL, a logistic regression model is fit using the covariates.
- propensity_model
Optional fitted propensity score model for P(A=1|X,S=1). If NULL, a logistic regression model is fit using source data.
- outcome_model
Optional fitted outcome model for E[L(Y,g)|X,A,S]. If NULL, a regression model is fit using the relevant data. For binary outcomes, this should be a model for E[Y|X,A] (binomial family). For continuous outcomes, this should be a model for E[L|X,A] (gaussian family).
- n_thresholds
Integer specifying the number of thresholds to evaluate. Thresholds are evenly spaced between 0 and 1. Default is 201.
- thresholds
Optional numeric vector of specific thresholds to use. If provided, overrides
n_thresholds.- include_naive
Logical indicating whether to also compute the naive ROC curve for comparison. Default is TRUE.
- ...
Additional arguments passed to internal functions.
Value
An object of class c("tr_roc", "roc_curve") containing:
- thresholds
Thresholds used
- sensitivity
Sensitivity (TPR) at each threshold
- fpr
False positive rate at each threshold
- specificity
Specificity at each threshold
- naive_sensitivity
Naive sensitivity (if include_naive=TRUE)
- naive_fpr
Naive FPR (if include_naive=TRUE)
- auc
Area under the ROC curve (computed via trapezoidal rule)
- naive_auc
Naive AUC (if include_naive=TRUE)
- estimator
Estimator used
- analysis
Analysis type
- n_source
Number of source observations
- n_target
Number of target observations
- treatment_level
Treatment level (NULL for factual mode)
Details
The ROC curve plots sensitivity (true positive rate) against the false positive rate (1 - specificity) at various classification thresholds.
Counterfactual Mode (treatment provided)
When treatment is specified, computes the ROC curve for counterfactual
outcomes under a hypothetical intervention.
Factual Mode (treatment = NULL)
When treatment is NULL, computes the ROC curve for observed outcomes
in the target population using inverse-odds weighting based on the
selection model only.
This function computes transportable sensitivity and FPR at multiple
thresholds using the estimators from tr_sensitivity() and tr_fpr().
The area under the curve (AUC) is computed using the trapezoidal rule on
the discrete threshold grid. For exact AUC estimation, use tr_auc()
which employs the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney statistic.
For efficient computation, all thresholds are evaluated in a single pass through the data, with nuisance models fitted only once.
References
Steingrimsson, J. A., et al. (2023). "Transporting a Prediction Model for Use in a New Target Population." American Journal of Epidemiology, 192(2), 296-304. doi:10.1093/aje/kwac128
Steingrimsson, J. A., Wen, L., Voter, S., & Dahabreh, I. J. (2024). "Interpretable meta-analysis of model or marker performance." arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.13458.
Examples
# Generate example data
set.seed(123)
n <- 500
x <- rnorm(n)
s <- rbinom(n, 1, plogis(0.5 - 0.3 * x))
a <- ifelse(s == 1, rbinom(n, 1, 0.5), rbinom(n, 1, plogis(-0.5 + 0.5 * x)))
y <- rbinom(n, 1, plogis(-1 + x - 0.5 * a))
pred <- plogis(-1 + 0.8 * x)
# Compute transportable ROC curve
roc <- tr_roc(
predictions = pred,
outcomes = y,
treatment = a,
source = s,
covariates = data.frame(x = x),
n_thresholds = 51
)
print(roc)
#>
#> Transportable ROC Curve
#> =======================
#>
#> Estimator: DR
#> Analysis: transport
#> Treatment level: 1
#> N (source): 309
#> N (target): 191
#> Thresholds evaluated: 51
#>
#> AUC: 0.7891
#> Naive AUC: 0.7842
#>
#> Use plot() to visualize the ROC curve.
#>
# Plot the ROC curve
plot(roc)